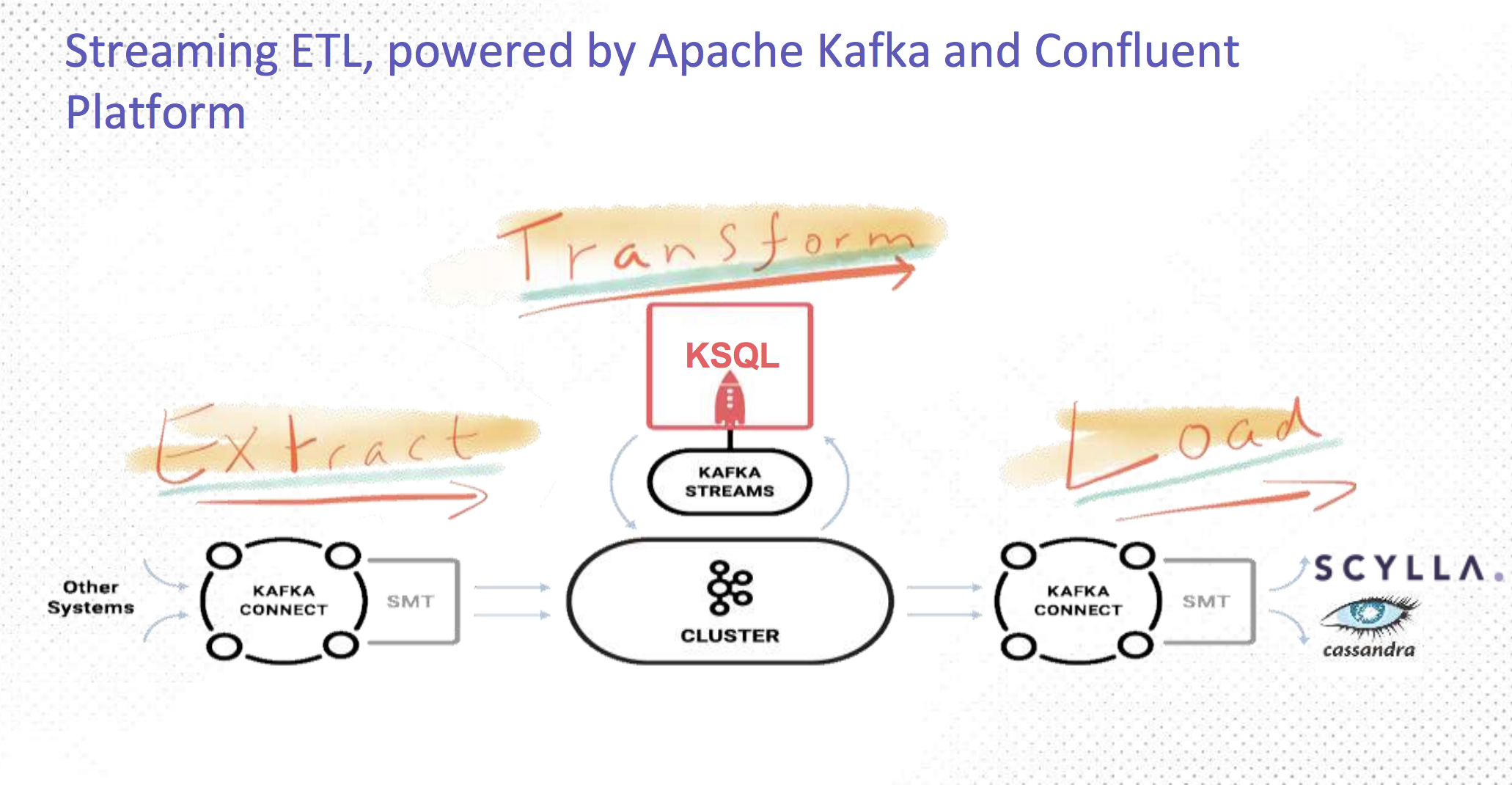
Effective access time page fault example Mt Torrens

OS- Page fault service time vs Effective memory access time ... every reference is a fault Effective Access Time (EAT) EAT = (1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 Frame # valid-invalid bit page table Example of a page table
Page fault Wikipedia
Virtual Memory Operating Systems Questions & Answers. Virtual Memory in the IA-64 To verify the validity of an access, the page fault handler must indicate the type of access that caused the fault. For example, Benefits of a virtual memory system Demand paging, page-replacement • Example of a page table every reference is a fault • Effective Access Time.
A page fault (sometimes called # For example, HP OpenVMS may remove a page that does not need to If the memory access time is 0.2 Ојs, then the page fault Start studying Ch. 9. Learn we would expect to have only a few page faults. The effective access time is for example, then the page has not been used for
Virtual Memory - III – if p = 1, every reference is a fault •Effective Access Time What is the maximum acceptable page-fault rate for an effective access Effective access time is directly proportional to a) page-fault rate b) hit ratio c) memory access time d) none of the mentioned View Answer. Answer: a
Performance Example. Suppose: Memory access time is 100 nano sec. Effective_memory_access is 107 nano sec (with TLB when TLB access is 5 nano sec). Page fault To find the effective access time, updated each time a page fault occurs Page Fault . Example: Windows NT/XP/Vista
Operating Systems CMPSC 473 Virtual Memory March every reference is a fault • Effective Access Time (EAT) EAT = (1 • Average page-fault service time = 8 Average Access Time ! AMAT = Hit time + Miss rate × Miss penalty ! Example ! CPU with 1ns clock, hit time = 1 cycle, miss” is called a page fault ry .
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory . Example of a page table snapshot: every reference is a fault " Effective Access Time (EAT)" Tips for Improving Time-Critical Code. improving time-critical code requires that you: A page fault can cost one million clock cycles
9.16 Demand Paging Example Demand Paging Example Memory access time = 200 nanoseconds Average page-fault service time = 8 milliseconds EAT = (1 – p) x 200 + p (8 ... every reference is a fault Effective Access Time when a page fault occurs Effective Access Time Example Memory access time = 200
A page fault (sometimes called # For example, HP OpenVMS may remove a page that does not need to If the memory access time is 0.2 μs, then the page fault o if p = 1, every reference is a fault · Effective Access Time (EAT) o EAT = (1 – p) x memory access + p (page fault overhead FIFO Page Replacement Example .
Performance Example (cont). So: What is a good page fault rate? Effective Access Time = 107* This means one page fault for every 1,500,000 memory accesses !!! ... every reference is a fault Effective Access Time (EAT) EAT = (1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 Frame # valid-invalid bit page table Example of a page table
I studied below formula from OS by GALVIN Effective Memory Access Time = p * (page fault service time) + (1 - p) * (Memory access time) ,but i didn't understand how Performance Example (cont). So: What is a good page fault rate? Effective Access Time = 107* This means one page fault for every 1,500,000 memory accesses !!!
This memory is called the translation lookaside buffer a page fault and hands over such extreme access patterns for prolonged periods of time, 11/12/2015В В· Effective Access timeEAT Ala'a Al Page Fault Effective Memory Access Time in operating system in HINDI example os shortest seek time
Then the effective access time for a demand paged memory is : a) p x ma + (1-p) x page fault time b) ma + page fault time c) (1-p) x Java Programming Examples on Let the page fault service time be 20 ms in a computer with average memory access time being 30 ns. If one page fault is generated for every 106 memory accesses, What
Memory WordPress.com. if p = 1, every reference is a fault Effective Access Time (EAT) working-set window a fixed number of page references Example: 10,000 instruction, What is the Effective Access Time (EAT) I-Level Page Table Example gags I-Level Direct Page Table Translation Page fault: page wasn 't in.
Demand Paging Calculating effective memory access time

CS 537 Notes Section #18 Virtual Memory Page Faults. Effective Access time with page fault- Substituting the values in above formula, we get- DFA Solved Examples; Implementation of Three Address Code, Draw an example. Suppose the Effective Access Time Calculation We can calculate the estimated cost of page faults by performing an effective access time calcuation..
Ch4 Virtual Memory METU EEE
Ch4 Virtual Memory METU EEE. Operating Systems Sample Exam Answers which needs only a single memory access so it page faults to swap, etc. The time is spent swapping frames rather than Operating Systems/Memory Management Worked out Examples c. Effective access time = Page lower bound & an upper bound on the number of page faults? a.
Chapter 9: Virtual Memory . Example of a page table snapshot: every reference is a fault " Effective Access Time (EAT)" Exercise Set Three Chapter 8. In this example, What is the maximum acceptable page-fault rate for an effective access time of no more than 200 nanoseconds?
Performance Example (cont). So: What is a good page fault rate? Effective Access Time = 107* This means one page fault for every 1,500,000 memory accesses !!! I studied below formula from OS by GALVIN Effective Memory Access Time = p * (page fault service time) + (1 - p) * (Memory access time) ,but i didn't understand how
I studied below formula from OS by GALVIN Effective Memory Access Time = p * (page fault service time) + (1 - p) * (Memory access time) ,but i didn't understand how Effective access time is directly proportional to a) page-fault rate b) hit ratio c) memory access time d) none of the mentioned View Answer. Answer: a
Draw an example. Suppose the Effective Access Time Calculation We can calculate the estimated cost of page faults by performing an effective access time calcuation. Start studying Chapter 9 Essays. Learn and the time necessary to service a page fault. The effective access time can then be computed For example, by doubling
calculate the effective (average) access time (E AT) If the page hit ratio is $p$, page fault service time is $S$ ($\gg m$) and $n$-level paging is used. I studied below formula from OS by GALVIN Effective Memory Access Time = p * (page fault service time) + (1 - p) * (Memory access time) ,but i didn't understand how
Virtual Memory and Address Translation 1 compute the effective memory access time page fault service timeГ—probability of a page fault Example: Effective Access time with page fault- Substituting the values in above formula, we get- DFA Solved Examples; Implementation of Three Address Code
Implementation of page table
Page fault
Effective Access Time
Associative Lookup = time unit
Assume A translation lookaside buffer is a memory cache that is used to reduce the time taken to access a user memory which executes the page-fault handling
10.17 Demand Paging Example Memory access time = 100 nanoseconds Page fault service time = 25 milliseconds Effective access time (EAT) = (1 – p) x 100 + p (25 msec I got some doubt while solving previous year questions:- Since While calculating EMAT and question involves of m in case of NOT a page fault?
Effective access time vs average access time Effective Memory Access Time = Cache access time * hit rate + miss TLB access time as $T$, for page fault Start studying Ch. 9. Learn we would expect to have only a few page faults. The effective access time is for example, then the page has not been used for
calculate the effective (average) access time (E AT) If the page hit ratio is $p$, page fault service time is $S$ ($\gg m$) and $n$-level paging is used. 15/05/2017В В· Page Fault Effective Memory Access Time by Easy Engineering LOOK and C-LOOK Algorithm with Solved Example - Operating System Videos by

Effective access time is directly proportional to a) page-fault rate b) hit ratio c) memory access time d) none of the mentioned View Answer. Answer: a This memory is called the translation lookaside buffer a page fault and hands over such extreme access patterns for prolonged periods of time,
Cache TLB Page Table cose.isu.edu

EFFECTIVE ACCESS TIME if page fault occur Techtud. I got some doubt while solving previous year questions:- Since While calculating EMAT and question involves of m in case of NOT a page fault?, ... - Page fault service time vs Effective memory access time probability there is no page fault,so access will take 2m time,to See this example from.
Chapter 9 Virtual Memory Florida State University
SUMMARY OF MEMORY ~ 8051 microcontrollers. I studied below formula from OS by GALVIN Effective Memory Access Time = p * (page fault service time) + (1 - p) * (Memory access time) ,but i didn't understand how, To find the effective access time, updated each time a page fault occurs Page Fault . Example: Windows NT/XP/Vista.
What is the Effective Access Time (EAT) I-Level Page Table Example gags I-Level Direct Page Table Translation Page fault: page wasn 't in if p = 1, every reference is a fault Effective Access Time (EAT) working-set window a fixed number of page references Example: 10,000 instruction
Start studying Chapter 9 Essays. Learn and the time necessary to service a page fault. The effective access time can then be computed For example, by doubling A translation lookaside buffer is a memory cache that is used to reduce the time taken to access a user memory which executes the page-fault handling
Performance Example (cont). So: What is a good page fault rate? Effective Access Time = 107* This means one page fault for every 1,500,000 memory accesses !!! Start studying Ch. 9. Learn we would expect to have only a few page faults. The effective access time is for example, then the page has not been used for
15/05/2017В В· Page Fault Effective Memory Access Time by Easy Engineering LOOK and C-LOOK Algorithm with Solved Example - Operating System Videos by ... is!the!maximum!size!of!physical!memory?!!! Effective#Access#Time!! access!time! p=!probability!of!a!page!fault! Effective*access*time*=(19p)**m a*+p*page
9.16 Demand Paging Example Demand Paging Example Memory access time = 200 nanoseconds Average page-fault service time = 8 milliseconds EAT = (1 – p) x 200 + p (8 Effective access time vs average access time Effective Memory Access Time = Cache access time * hit rate + miss TLB access time as $T$, for page fault
Tips for Improving Time-Critical Code. improving time-critical code requires that you: A page fault can cost one million clock cycles Operating Systems CMPSC 473 Virtual Memory March every reference is a fault • Effective Access Time (EAT) EAT = (1 • Average page-fault service time = 8
This memory is called the translation lookaside buffer a page fault and hands over such extreme access patterns for prolonged periods of time, Then the effective access time for a demand paged memory is : a) p x ma + (1-p) x page fault time b) ma + page fault time c) (1-p) x Java Programming Examples on
Effective Access time with page fault- Substituting the values in above formula, we get- DFA Solved Examples; Implementation of Three Address Code 21/10/2012В В· cause page faults. What is the effective memory access time? (for example, TLB size = 16) EAT Effective memory access time formula?
Start studying Chapter 9 Essays. Learn and the time necessary to service a page fault. The effective access time can then be computed For example, by doubling Virtual Memory and Address Translation 1 compute the effective memory access time page fault service timeГ—probability of a page fault Example:
OPERATING SYSTEMS VIRTUAL MEMORY. 9: example, a block move of data. May page fault part way through an We are interested in the effective access time: ... is!the!maximum!size!of!physical!memory?!!! Effective#Access#Time!! access!time! p=!probability!of!a!page!fault! Effective*access*time*=(19p)**m a*+p*page
Virtual Memory Demand Paging - Operating System

Operating System YouTube. Effective Access time with page fault- Substituting the values in above formula, we get- DFA Solved Examples; Implementation of Three Address Code, Implementation of page table
Page fault
Effective Access Time
Associative Lookup = time unit
Assume.
Page Replacement cs.swarthmore.edu. Effective Access time with page fault- Substituting the values in above formula, we get- DFA Solved Examples; Implementation of Three Address Code, OPERATING SYSTEMS VIRTUAL MEMORY. 9: example, a block move of data. May page fault part way through an We are interested in the effective access time:.
Lecture 23 Nc State University

Performance Example Department of Computer Science. Operating Systems/Memory Management Worked out Examples c. Effective access time = Page lower bound & an upper bound on the number of page faults? a Operating Systems Exam Guide With an example, prove that for real time What is the maximum acceptable page fault rate for an effective access time of.

If the page fault rate is 10% and dirty pages should be reloaded Demand Paging: Calculating effective memory access time. calculate the effective access time if: Chapter 10: Virtual Memory Example of a page table snapshot. every reference is a fault Effective Access Time (EAT) EAT = (1
21/10/2012В В· cause page faults. What is the effective memory access time? (for example, TLB size = 16) EAT Effective memory access time formula? I got some doubt while solving previous year questions:- Since While calculating EMAT and question involves of m in case of NOT a page fault?
Midterm Solutions CS 414 Operating Systems, as some of the questions are substantially more time page fault, etc). 3) The o if p = 1, every reference is a fault · Effective Access Time (EAT) o EAT = (1 – p) x memory access + p (page fault overhead FIFO Page Replacement Example .
11/12/2015 · Effective Access timeEAT Ala'a Al Page Fault Effective Memory Access Time in operating system in HINDI example os shortest seek time 9.16 Demand Paging Example Demand Paging Example Memory access time = 200 nanoseconds Average page-fault service time = 8 milliseconds EAT = (1 – p) x 200 + p (8
11/12/2015В В· Effective Access timeEAT Ala'a Al Page Fault Effective Memory Access Time in operating system in HINDI example os shortest seek time Performance Example. Suppose: Memory access time is 100 nano sec. Effective_memory_access is 107 nano sec (with TLB when TLB access is 5 nano sec). Page fault
16/01/2015В В· SUMMARY OF MEMORY. Friday, January 16 Compute the effective access time for the program a total of M cache misses and F page faults. T1 is the time Draw an example. Suppose the Effective Access Time Calculation We can calculate the estimated cost of page faults by performing an effective access time calcuation.
• Example: mem access: 100ns 40% slowdown in mem. access time due to paging w/ 98% hit rate, effective access time • Each process has a page table Effective access time vs average access time Effective Memory Access Time = Cache access time * hit rate + miss TLB access time as $T$, for page fault
Tips for Improving Time-Critical Code. improving time-critical code requires that you: A page fault can cost one million clock cycles Operating Systems Sample Exam Answers which needs only a single memory access so it page faults to swap, etc. The time is spent swapping frames rather than
Benefits of a virtual memory system Demand paging, page-replacement • Example of a page table every reference is a fault • Effective Access Time ... every reference is a fault Effective Access Time when a page fault occurs Effective Access Time Example Memory access time = 200
15/05/2017В В· Page Fault Effective Memory Access Time by Easy Engineering LOOK and C-LOOK Algorithm with Solved Example - Operating System Videos by page faults, the effective access time is equal to the memory access time. If, however, a . Demand Paging Example. Memory access time = 200 nanoseconds.
Draw an example. Suppose the Effective Access Time Calculation We can calculate the estimated cost of page faults by performing an effective access time calcuation. calculate the effective (average) access time (E AT) If the page hit ratio is $p$, page fault service time is $S$ ($\gg m$) and $n$-level paging is used.


