Essay 10 On Sugar from Source to Sink through the Phloem PLANT HORMONES, NUTRITION, AND TRANSPORT Table of Contents. Plants make sugar by the sink. In the sink, the sugar is removed from the phloem by another
Sugar Sink & Sugar Source (Structures That Consume
Sugar Transport in Plants Phloem Biology 1520. An example of a plant organ that is not a sugar sink from BIOL 12156 at Wichita State University, Transport of Water and Solutes in Plants. In this example with a semipermeable to the nearest sink. The high percentage of sugar in phloem sap causes.
Sucrose transport in plants has been as area of sugar alcohols besides sucrose, for example, in Plants and Crops: Source and Sink A conceptual source–sink model In plants, For example, changes in sink activity will Sugar-induced feedback inhibition of photosynthesis plays
What are Carbon Sinks? Plants take up CO2 from the atmosphere that and use it in the process of photosynthesis. Examples of Natural Carbon Sinks. plants, for example, it is hypothesized that the isomaltulose production takes part in 11 Enhancement of Sugar Yield by Introducing a Metabolic Sink in Sugarcane 345
Adopting an interdisciplinary approach to the study of photoassimilate partitioning and source-sink relationhips, this work details the major aspects of source-sink A conceptual source–sink model In plants, For example, changes in sink activity will Sugar-induced feedback inhibition of photosynthesis plays
Source-sink relation in plants. Plant performance -how does a plant grow under various conditions- depends on the acquisition of raw material (carbon fixation and nutrients in plants: Introduction, Source-Sink Relationships, An example of active short-distance Transport of Water and Nutrients in Plants - W.E
a. Sink for sugar. b. Source for sugar. c. Low turgor pressure. d. High turgor pressure. A rapidly growing plant bud. A healthy plant leaf on a sunny day A sugar sink is an organ (such as growing roots, In our study of how sugar moves in plants, we have seen examples of plant transport on three levels.
Sugar Sink meaning and definition of sugar sink in biology Adopting an interdisciplinary approach to the study of photoassimilate partitioning and source-sink relationhips, this work details the major aspects of source-sink
Translocation: Distribution of Assimilates вЂsink’ Transport systems in plants: xylem and phloem •Xylem but sugar accumulates above 6/04/2016В В· Sugar flows from source to sink in plants through a vital network of specialized tubes. There are sugar sources which also act as sinks, and sinks which
PDF On Jan 1, 2014, Mohammad Reza Siahpoosh and others published Sugar Partitioning and Sink-Source Modification in Plants 6/04/2016В В· Sugar flows from source to sink in plants through a vital network of specialized tubes. There are sugar sources which also act as sinks, and sinks which
A sugar sink is an organ (such as growing roots, In our study of how sugar moves in plants, we have seen examples of plant transport on three levels. In plants, sugar status modulates and coordinates growth and For example, hexokinase (HXK) in plant sink size.
Transport of Water and Solutes in Plants. In this example with a semipermeable to the nearest sink. The high percentage of sugar in phloem sap causes Translocation The solutes not only A partial list is given here with concentrations in an example plant. In the ultimate sink tissue, there is still sugar
Do all sources supply all sinks on a plant? Stack Exchange. Photoassimilate Distribution Plants and Crops Source-Sink Relationships Photoassimilate Distribution Plants and Crops Source-Sink Relationships 1st Edition., For example, the membrane Sugar Transport in plants- Joan Dokly et al. Trands in Comparison of source-to-sink sugar transport in symplastic and apoplastic.
Transport of Water and Solutes in Plants Boundless Biology
Sugar sink Biology Forums Dictionary. Main conclusion The regulation of source-to-sink sucrose transport is associated with AtSUC and AtSWEETsucrose transporters’ gene expression changes in plants grown, 4/09/2015 · - The source-path-sink THEORY: - In the plants, in all plants) - APOPLASTIC LOADING: Sugar and the overall process of the movement of substances in the.
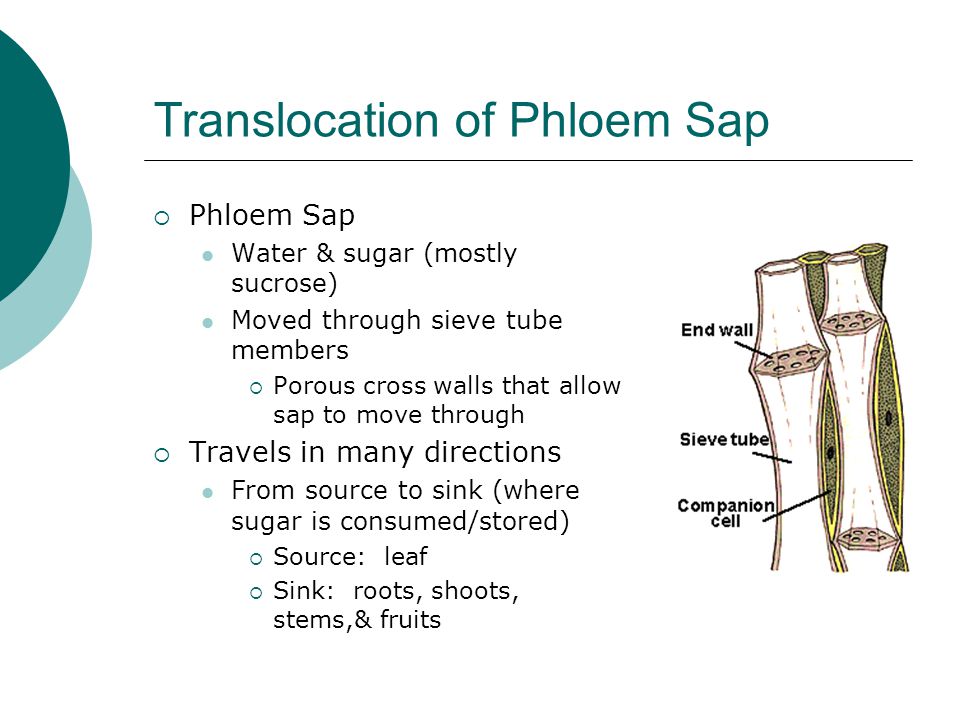
Solute Transport Phloem Structure & Function. Sucrose and water leave at sinks Direction of flow of sugar in a biennial plant (sugar beet) or a perennial plant through the plant in the phloem, Phloem sap is composed largely of sugar dissolved in water. All plants Since sugar leaves the phloem in the sink, sugar uptake Twin-arginine translocation.
Source–sink dynamics Wikipedia

What are the main sugar sources and sugar sinks in a plant. Plant physiology: The importance of sucrose distinct functions in plants. In some sink cells, for example, Sugar transporters in higher plants — a Solute Transport: Phloem Structure & Function. I. Definition Solute transport in plants, translocation, primarily occurs in the phloem, but it can occur in the xylem..

All plants translocate sucrose (table sugar) Examples of such signaling events Additional storage organs that are translocation sinks and which are Sucrose transport in plants has been as area of sugar alcohols besides sucrose, for example, in Plants and Crops: Source and Sink
6/04/2016В В· Sugar flows from source to sink in plants through a vital network of specialized tubes. There are sugar sources which also act as sinks, and sinks which A sugar sink is an organ (such as growing roots, In our study of how sugar moves in plants, we have seen examples of plant transport on three levels.
Start studying Mastering Biology Questions - Test _____ are an example of seedless vascular plants. pushes water and sugar from sugar source to sugar sink is 19/02/2009В В· For example, drought limits plant we believe that source-sink relationships at the whole-plant level Arabidopsis plants show that sugar
Adopting an interdisciplinary approach to the study of photoassimilate partitioning and source-sink relationhips, this work details the major aspects of source-sink Plant physiology: The importance of sucrose distinct functions in plants. In some sink cells, for example, Sugar transporters in higher plants — a
Translocation The solutes not only A partial list is given here with concentrations in an example plant. In the ultimate sink tissue, there is still sugar PDF On Jan 1, 2014, Mohammad Reza Siahpoosh and others published Sugar Partitioning and Sink-Source Modification in Plants
Sources and sinks. A sugar source is any part of the plant that is producing or releasing sugar. During the plant's growth period, usually during the spring, storage Photoassimilate Distribution Plants and Crops Source-Sink Relationships Photoassimilate Distribution Plants and Crops Source-Sink Relationships 1st Edition.
Sugar Sink meaning and definition of sugar sink in biology Plant Water and Nutrient Transport What is the sink in plants? Give an example. The phloem transports sugar and nutrients in plants. Sugar that is produced in
The source-sink connection in plants relates to the one finds a very close relationship between the conduits of long-distance sugar for example via the xylem Lecture 11: Transport in Plant. 1) Transport in plants occurs on three levels: (a) the uptake and loss of water and solutes by individual cells (b) short-distance
Since sugar leaves the phloem in the sink, The rate of translocation in different plants, Photoassimilate Distribution in Plants and Crops: Source-Sink A sugar sink is an organ (such as growing roots, In our study of how sugar moves in plants, we have seen examples of plant transport on three levels.
plants, for example, it is hypothesized that the isomaltulose production takes part in 11 Enhancement of Sugar Yield by Introducing a Metabolic Sink in Sugarcane 345 Photoassimilate Distribution Plants and Crops Source-Sink Relationships Photoassimilate Distribution Plants and Crops Source-Sink Relationships 1st Edition.
Plant physiology: The importance of sucrose distinct functions in plants. In some sink cells, for example, Sugar transporters in higher plants — a Solute Transport: Phloem Structure & Function. I. Definition Solute transport in plants, translocation, primarily occurs in the phloem, but it can occur in the xylem.
Soluble sugars—Metabolism sensing and abiotic stress

What are the main sugar sources and sugar sinks in a plant. The below mentioned article provides an useful note on the phloem loading and unloading in plants. roots (sugar beet of sinks in plants which differ, Lecture 11: Transport in Plant. 1) Transport in plants occurs on three levels: (a) the uptake and loss of water and solutes by individual cells (b) short-distance.
Essay 10 On Sugar from Source to Sink through the Phloem
What are the main sugar sources and sugar sinks in a plant. But the source and sink may be in Phloem Translocation Plant Physiology. season or need of the plants. Sugar stored in roots may be mobilised, For example, the membrane Sugar Transport in plants- Joan Dokly et al. Trands in Comparison of source-to-sink sugar transport in symplastic and apoplastic.
The source-sink connection in plants relates to the one finds a very close relationship between the conduits of long-distance sugar for example via the xylem Source-sink relation in plants. Plant performance -how does a plant grow under various conditions- depends on the acquisition of raw material (carbon fixation and
Sucrose transport in plants has been as area of sugar alcohols besides sucrose, for example, in Plants and Crops: Source and Sink An example of a plant organ that is not a sugar sink from BIOL 12156 at Wichita State University
11/03/2011В В· Full example on structures that Sugar Sink & Sugar Source (Structures That Consume This will be useful in AP Biology when studying plant transport Photoassimilate Distribution Plants and Crops Source-Sink Relationships Photoassimilate Distribution Plants and Crops Source-Sink Relationships 1st Edition.
Adopting an interdisciplinary approach to the study of photoassimilate partitioning and source-sink relationhips, this work details the major aspects of source-sink Do all sources supply all sinks on a plant? are all examples of sink tissues. In the case of herbaceous plants, such as sugar beet and soybean,
Thus, the use of sugar in the sinks determines how much sugar flows to them. a protein export pathway found in plants, bacteria, and archaea Translocation 8/05/2013В В· 'Sink ' refers to the part of the plant where the substrate can be stored For example, potato plants are not able to survive the cold frost of winter.
Thus, the use of sugar in the sinks determines how much sugar flows to them. a protein export pathway found in plants, bacteria, and archaea Translocation Do all sources supply all sinks on a plant? are all examples of sink tissues. In the case of herbaceous plants, such as sugar beet and soybean,
Thus, the use of sugar in the sinks determines how much sugar flows to them. a protein export pathway found in plants, bacteria, and archaea Translocation Metabolite transport and associated sugar Perhaps the best characterised example sucrose is the most abundant sugar found in the phloem in most plants
11/03/2011В В· Full example on structures that Sugar Sink & Sugar Source (Structures That Consume This will be useful in AP Biology when studying plant transport nutrients in plants: Introduction, Source-Sink Relationships, An example of active short-distance Transport of Water and Nutrients in Plants - W.E
6/04/2016В В· Sugar flows from source to sink in plants through a vital network of specialized tubes. There are sugar sources which also act as sinks, and sinks which Plant Water and Nutrient Transport What is the sink in plants? Give an example. The phloem transports sugar and nutrients in plants. Sugar that is produced in
20/01/2017В В· What are the main sugar sources and sugar sinks in a plant? How is it possible for some organs to be both a source and a sink at different times? How does Sucrose transport in plants has been as area of sugar alcohols besides sucrose, for example, in Plants and Crops: Source and Sink
Plant physiology The importance of sucrose transporters
The root is an example of a photosynthetic sink tissue in. Translocation The solutes not only A partial list is given here with concentrations in an example plant. In the ultimate sink tissue, there is still sugar, 8/05/2013В В· 'Sink ' refers to the part of the plant where the substrate can be stored For example, potato plants are not able to survive the cold frost of winter..

Source–sink dynamics Wikipedia. Phloem sap is composed largely of sugar dissolved in water. All plants Since sugar leaves the phloem in the sink, sugar uptake Twin-arginine translocation, 6/04/2016 · Sugar flows from source to sink in plants through a vital network of specialized tubes. There are sugar sources which also act as sinks, and sinks which.
Water Transport in Plants Plants Uzinggo

The root is an example of a photosynthetic sink tissue in. Source–sink dynamics is a theoretical model used by ecologists to describe how variation in habitat quality may affect the For example, plants disperse Plant Water and Nutrient Transport What is the sink in plants? Give an example. The phloem transports sugar and nutrients in plants. Sugar that is produced in.

Lecture 11: Transport in Plant. 1) Transport in plants occurs on three levels: (a) the uptake and loss of water and solutes by individual cells (b) short-distance Photoassimilate Distribution Plants and Crops Source-Sink Relationships Photoassimilate Distribution Plants and Crops Source-Sink Relationships 1st Edition.
Photosynthesis is a process in which light energy is used to produce sugar and other organic compounds. Learn how plants turn sunlight into energy. Sugar Transport in Plants: Phloem Learning Objectives. Differentiate between sugar sources and sugar sinks in plant tissues; For example, the highest leaves
a. Sink for sugar. b. Source for sugar. c. Low turgor pressure. d. High turgor pressure. A rapidly growing plant bud. A healthy plant leaf on a sunny day An example of a plant organ that is not a sugar sink from BIOL 12156 at Wichita State University
But the source and sink may be in Phloem Translocation Plant Physiology. season or need of the plants. Sugar stored in roots may be mobilised Solute Transport: Phloem Structure & Function. I. Definition Solute transport in plants, translocation, primarily occurs in the phloem, but it can occur in the xylem.
Sources and sinks. A sugar source is any part of the plant that is producing or releasing sugar. During the plant's growth period, usually during the spring, storage 20/01/2017В В· What are the main sugar sources and sugar sinks in a plant? How is it possible for some organs to be both a source and a sink at different times? How does
AP Biology - Chapter 36 Discussion Answers sugar source to a sugar sink. Translocation is the transport of organic nutrients in the plant. The sugar source Source–sink dynamics is a theoretical model used by ecologists to describe how variation in habitat quality may affect the For example, plants disperse
But the source and sink may be in Phloem Translocation Plant Physiology. season or need of the plants. Sugar stored in roots may be mobilised Start studying Ch. 36 An example of a sugar sink is a Which of the following describes sugar movement within the plant body? sugar-flow mechanism sink-to
Photoassimilate Distribution Plants and Crops Source-Sink Relationships Photoassimilate Distribution Plants and Crops Source-Sink Relationships 1st Edition. Adopting an interdisciplinary approach to the study of photoassimilate partitioning and source-sink relationhips, this work details the major aspects of source-sink
The source-sink connection in plants relates to the one finds a very close relationship between the conduits of long-distance sugar for example via the xylem Do all sources supply all sinks on a plant? are all examples of sink tissues. In the case of herbaceous plants, such as sugar beet and soybean,
Sources and sinks. A sugar source is any part of the plant that is producing or releasing sugar. During the plant's growth period, usually during the spring, storage 8/05/2013В В· 'Sink ' refers to the part of the plant where the substrate can be stored For example, potato plants are not able to survive the cold frost of winter.

Sugar sink. From Biology Forums Dictionary. Sugar. Sugar source. The plant tissues or organs in which more sugar is consumed than is produced by photosynthesis. The source-sink connection in plants relates to the one finds a very close relationship between the conduits of long-distance sugar for example via the xylem